
Symbol relating the hydrogen ion concentration or activity of a solution to that of a standard solution approximately equal to the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. Oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry Oxygen saturation of the hemoglobin of arterial blood The term formerly used ( A-a D O 2) is discouraged.Īlveolar-arterial tension ratio P aO 2: P AO 2 The term oxygen exchange index describes this ratio.
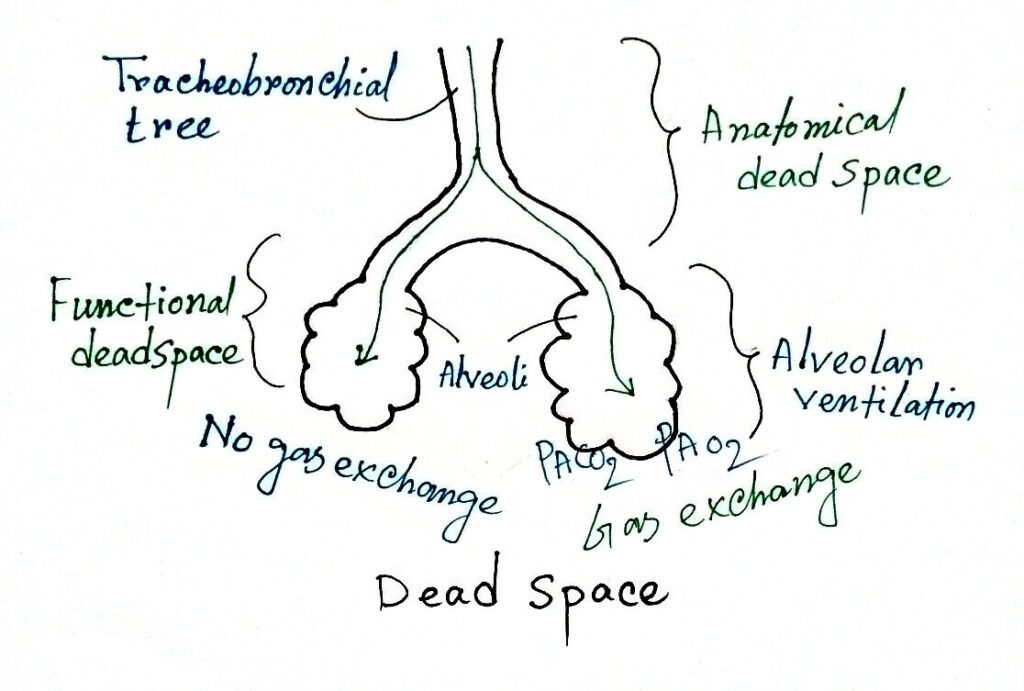
Positive pressure ventilation (i.e.Inhaled air not part of gas exchange Blood gas, acid-base, and gas exchange terms P aO 2Īrterial oxygen tension, or partial pressureĪlveolar oxygen tension, or partial pressureĪrterial carbon dioxide tension, or partial pressureĪlveolar carbon dioxide tension, or partial pressureĪlveolar-arterial oxygen tension difference. Neck extension and jaw protrusion (can increase it twofold). General anesthesia – multifactorial, including loss of skeletal muscle tone and bronchoconstrictor tone. The ratio of physiologic dead space to tidal volume is usually about 1/3. Alveolar dead space is the volume of gas within unperfused alveoli (and thus not participating in gas exchange either) it is usually negligible in the healthy, awake patient. Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone (as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zones) and includes the trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles it is approximately 2 mL/kg in the upright position. Physiologic or total dead space is the sum of anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space. 
Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
